ExpressionScript - プレゼンテーション
From LimeSurvey Manual
はじめに
LimeSurveyでは、新しいExpressionScript(ES)モジュールを使用して、より複雑な分岐、評価、検証、および文言調整がサポートされています。LimeSurveyがサーバー内で行う置換、条件、評価の管理方法を置き換えることができます。また、ランタイムデータベースの読み込みのほとんどが不要になるため、処理速度が大幅に向上します。ESはDr. Thomas White(TMSWhite)が開発しました。
主な定義
- 式: 中括弧で囲まれたもの:
- 中括弧の内側の先頭または末尾に空白があってはならない
- 式の内容はEMによって評価されるため、数式、関数、複雑な文字列および日付処理を含めることが可能
- 文言調整: "パイピング"と呼ぶこともある。条件によってテキストを変更するプロセス:
- すべての'置換フィールド'、参加者データ、回答データにアクセス可能
- 質問、回答、およびそれらのプロパティに簡単にもアクセス可能
- 出現条件 式: 質問の表示可否を制御する新たな質問属性:
- 出現条件式がある場合、trueと判断された場合にのみ質問が表示される
- 内部的には、すべてのarray_filterおよびarray_filter_excludeコマンドがサブ質問レベルの出現条件となる
- SGQA (古い変数の命名方法):
- Survey-Group-Question-Answer(アンケート、グループ、質問、回答)の頭文字のこと
- SGQA変数名は、123X5X382X971のような形式で、サブ質問の接尾辞がついている場合もある
- これらの変数名は、その元になっているS/Q/G/Aデータベースコードに紐づいており、多くの場合変更する必要がある
- 式質問タイプ: 計算結果を保存したり、データベースに格納したりするための新しい質問タイプ:
- 固定的なテキストを表示する質問のようなもので、"この質問をいつも隠す"と設定してもデータベースに格納される
- 質問コード: EMでの使用が推奨される変数名:
- 質問の目的を示すわかりやすい名前にし、複雑なロジックの可読性を高めることが可能
- 質問コードは数字で始めることはできないので、質問番号を質問コードにするときは、"q1"、"q1a"、"g1q2"のようにする
- データをSPSSまたはRにエクスポートする際、これが変数名になるため、統計分析を行う場合は、ユニークにする必要がある
EMを使用する必要性
必ず使わなければならないわけではありません。作成するアンケートがどれだけ複雑かによって変わります。
例えば、条件エディターでは、アンケートの質問に適用できるいくつかの基本的な式を扱います。ただし、条件エディタには制限があります。EMが使用されているのはこのためです。EMがカスタマイズの可能性を広げています。
条件と出現条件式の両方を使えるか?
はい。質問によって条件エディターを使用することも、出現条件式を使用することもできます。
条件と式の両方を同じ質問で設定することはできません。 条件が設定されると、出現条件のフィールドに書き込まれた式は使われません。さらに、出現条件式フィールドは手動では編集できません。
しかし、質問内で式と条件の両方を使用する方法があります。上で述べたように、条件式は出現条件式のフィールドを置き換えます。完了したら、新しく作成された式を確認し、テキストエディターにコピーします。条件エディターで作成した条件を削除し、残りの式と一緒にテキストエディターにコピーした条件ベースの式を追加して質問を編集します。
条件と出現条件のどちらを選ぶべきか?
各々の長所と短所のリストを以下に示します。
| スタイル | 長所 | 短所 |
|---|---|---|
| 条件 | 1. シンプルな条件を作成するための優れたGUI 2. 文書化が容易でサポートチームが理解しやすいGUI |
1. 簡単な比較のみをサポートし、"AND"/"OR"条件はうまく機能しない 2. カスケード条件が不安定 3. データベースに負荷がかかり、長いアンケートが重くなる 4. 条件のリロードにかかる不具合が報告されている 5. GUIに拡張性がなく、何十、何百、または何千もの質問があるときにうまくいかない 6. SGQA名を使用しなければならないので、紙ベースのアンケートを変換するのが遅くなることがある 7. 複雑な分岐が必要な場合、カスタムコードロジックを書くプログラマーが必要なことがある |
| 出現条件 | 1. 80以上の関数と数学/文字列演算子を含む非常に複雑なロジックをサポート 2. カスケードロジックの完全サポート 3. 高速 - 余計なデータベースアクセスがなく、多数の質問があるアンケートをサポート 4. SGQAコードを必要としないため、リロードロジックで問題が生じない 5. 構文ハイライト機能は多数の質問があるアンケートにも対応 6. 既存の紙ベースのアンケートの電子化に簡単かつ迅速に対応可能 7. 半構造化インタビューや疫学調査もプログラマーを必要とせず容易に作成可能 |
1. 単純な条件に適したGUIがない(代わりに構文ハイライト機能を使用) |
- ニーズに合ったものを使用することをお勧めします。
- EM機能の詳細については、こちらをクリックしてください。
はじめに
式マネージャーを始める最善の方法は以下のとおりです。
- https://www.limesurvey.org/en/download から最新の安定版をインストールする
- Import and explore some サンプルアンケートをインポートして確認する
- 使用例やHow-to、ステップバイステップの例を参照する
- EMに関するドキュメント(このページ)を読む
- 分離された式の単体テスト(高度)
- すべてのEM関数と演算子、PHPとJavaScriptの結果の使用例を表示
- PHPとJavaScriptのバージョンで異なる結果を生成する関数はほとんどないので、このページの内容を踏まえ、EMロジックを適切に計画することが可能
- 分離された式の単体テスト(高度)
用語
EMの機能を説明するため、以下の単語を使用します。
- 出現条件を基にした分岐 - 質問は出現条件を満たす場合のみ表示されます(出現条件を満たさない場合、表示されず、データベースにはNULLとして記録されます)。質問エディターパネルと質問グループエディターパネルに出現条件フィールドがあります。後者は、各質問に同じ条件をコピーしたり、グループと質問レベルの条件ロジックを組み合わせたりすることなく、一連の条件をグループ全体に適用するために使用します。
- 文言調整 - どの質問を使うかを決めたら、文言調整(パイピングとも言います)によって質問の文言を決定します。これは、単純な置換(例: {TOKEN:FIRSTNAME})をするだけでなく、性別や回答者の数に応じて語句を変化させることができます。また、他の質問に回答したか(または回答内容)に基づいて、配信するメッセージを変更することもできます。
- 式 - EMでは、式による演算結果を格納する質問タイプ式が新たに追加されました。演算結果は、たとえページ上で非表示であっても、データベースに書き込まれます。これにより、暗黙的なスコア計算、複雑な式に基づくナビゲーション、評価、およびレポートの作成・保存が可能になります。
出現条件とカスケードされた出現条件
すべての質問タイプで、質問が表示されるかどうかを制御する出現条件オプション が追加されました。EMは、アンケートに登場する順に出現条件式を処理します。式が真(または式がない - 古い形式のアンケート向け)の場合、質問が表示されます。出現条件式が偽の場合、質問は非表示になり、その値はデータベースでNULLになります。グループに出現条件を満たす質問がない場合、グループ全体がスキップされます。
さらに、式に含まれる変数のいずれかの出現条件が偽の場合、式は常に偽と評価されます。これにより出現条件の入れ子が可能になり、各々の質問に対して非常に長い出現条件の式を書く必要がなくなります。
たとえば、5つの質問Q1〜Q5があり、Q1に回答したらQ2、Q2に回答したらQ3、のように表示したいとします。出現条件の式は次のようになります。
| 質問コード | 出現条件 | 質問 |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 1 | 名前は何ですか。 |
| Q2 | Q1 | {Q1}さん、何歳ですか。 |
| Q3 | Q2 | {Q2}歳なのですね。結婚していますか。 |
| Q4 | Q3 == "Y" | {Q1}さん、結婚して何年になりますか。 |
| Q5 | Q4 | {Q1}さん、子供は何人いますか。 |
グループレベルの出現条件
ExpressionScriptは、グループレベルの出現条件もサポートしています。これにより、ループの実装が容易になります。例えば、最大10の事柄(製品や世帯の構成人員など)に関する情報を収集するため、まずその数を質問するとします(例えば、世帯の構成人数や、リストの中から好きな製品をいくつか選んでもらうなど)。後から繰り返し聞くべき回数が分かったら、10個用意したグループごとに{count>=1}、{count>=2}、... {count>=10}などのグループレベルの出現条件を設定することができます。それぞれのグループ内では、質問レベルの条件付きロジック(例:回答者の性別や年齢別の質問)を作成することができます。質問レベル、グループレベルの出現条件の式は、質問を表示すべきかを決定するため両方が使われます。
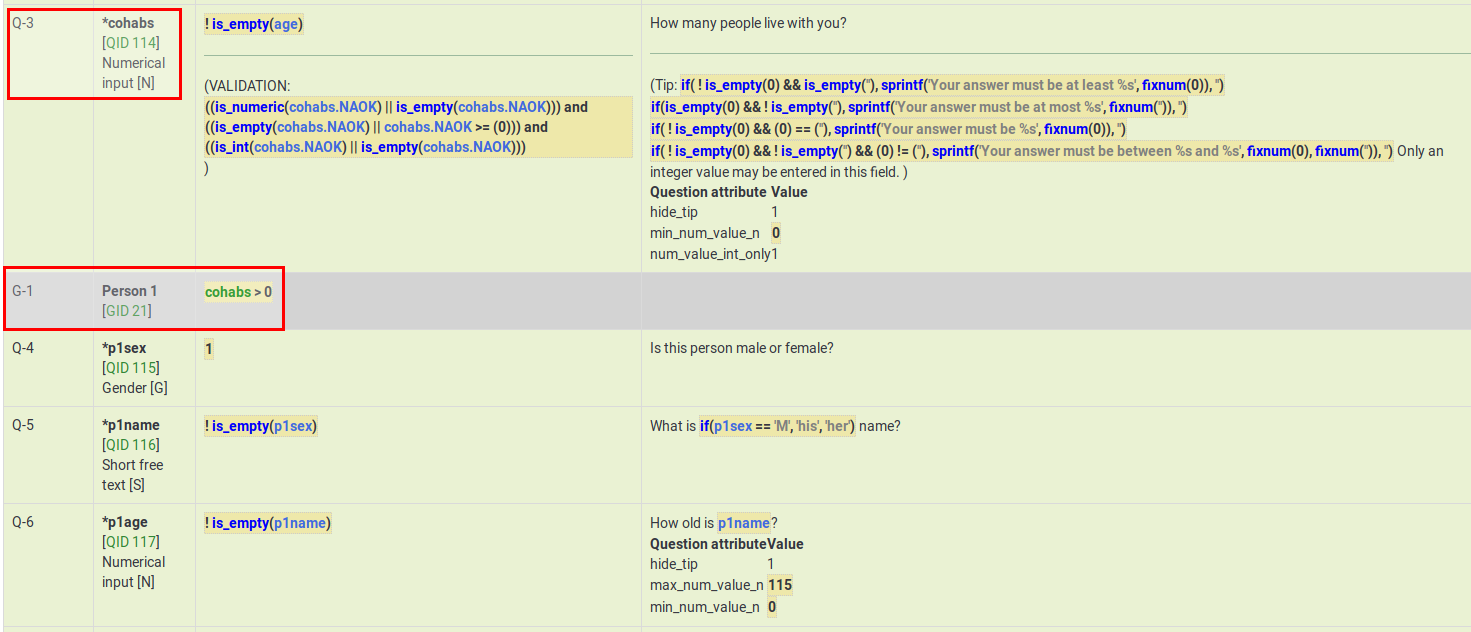
例を確認するには、次のアンケートをインポートします。国勢調査の例
以下のスクリーンショットでは、回答者が少なくとももう1人の同居者と一緒に住んでいる場合、グループPerson 1が表示されている(出現条件を満たしている)ことがわかります。
文言調整/パイプ
中括弧内のものはすべて式として扱われるようになりました(後述する例外が1つあります)。式はすべてのLimeReplacementFields、すべての変数(いくつかのエイリアスを介して)、すべての一般的な演算子(数学、論理、比較)、数多くの関数(クライアント側でも動的に機能する)にアクセスします。
これらの式を使用すると、次のようなことができます。
- 先行する質問への回答に基づいて文言調整されたメッセージを回答者に表示する
- 評価を作成し、その結果に基づいて評価結果を表示する(条件付きで分岐、またはメッセージを表示する)(評価モジュール自体は使用しない)
- 質問、回答、およびレポート内の動詞、名詞を変化させる
- アンケートの最後で、"回答を表示する"ページの前に回答の要約を表示する
式
式と呼ばれる新しい質問タイプがあります。これは、表示されている値をデータベースに格納することを除き、テキスト表示質問タイプと似ています。したがって、式の質問テキストに評価計算が含まれている場合、パブリックまたはプライベート統計情報内に表示できる変数の値がデータベースに格納されます。
構文
中カッコ内に含まれるものはすべて式と見なされます(ただし、先頭または末尾に空白があってはなりません。これは、ExpressionScript が埋め込みJavaScriptを処理しないようにするためです)。
開く括弧の後、閉じる括弧の前に空白がない限り、式は複数の行にまたがっても構いません。特に次のような入れ子のif()構文が見やすくなります。
{if(is_empty(PFTotals),
'',
if(PFTotals >= -5 && PFTotals <= -4,
'Very Soft',
if(PFTotals >= -3 && PFTotals <= -2,
'Soft',
if(PFTotals == -1,
'Somewhat Soft',
if(PFTotals == 0,
'Moderate',
if(PFTotals == 1,
'Somewhat Hard',
if(PFTotals >= 2 && PFTotals <= 3,
'Hard',
if(PFTotals >= 4 && PFTotals <= 5,
'Very Hard',
''
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)}
ExpressionScriptは次の構文をサポートしています。
- すべての標準的な数学演算子 (例: +,-,*,/,!)
- すべての標準的な比較演算子(例: <,<=,==,!=,>,>=, およびこれらと同等のもの: lt,le,eq,ne,gt,ge)
- 括弧(式のグルーピング)
- 条件演算子(例: &&,||, およびこれらと同等のもの: and,or)
- シングルクォートやダブルクォートで囲まれた文字列(それぞれが異なるクォートタイプの文字列を埋め込むことができます)
- コンマ演算子(式のリストを持つことができ、最終結果を返すことができます)
- 代入演算子(=)
- 定義済みの変数(質問、質問属性、回答を参照するため) - 例: すべてのSGQAコード
- 定義済みの関数(既に80以上ありますが、簡単に追加できます)
演算子
EM構文は、通常の演算子の優先順位に従います。
| レベル | 演算子 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | () | グループ化または関数呼び出しのための括弧 |
| 2 | ! - + | 単項演算子: 否定、正負 |
| 3 | * / | 乗算、除算 |
| 4 | + - | 加算、減算 |
| 5 | < <= > >= lt le gt ge | 比較演算子 |
| 6 | == != eq ne | 同等比較 |
| 7 | and | 論理積 AND |
| 8 | or | 論理和 OR |
| 9 | = | 代入演算子 |
| 10 | , | コンマ演算子 |
番号と文字列の不一致およびアルファベット/数字の比較に関する注意
値を不等号や等号で比較する場合は、値の型の不一致に注意してください。ユーザーが入力した値や選択した回答コードが明確に数値であれば、数値として使用されます。
いずれかの値が"で囲まれている場合は、文字列としての比較が行われます。数値として比較したい場合は"で囲んではいけません。
たとえば、Q0.NAOKが数値質問で値が9である場合、Q0.NAOK > "50"はtrueとなります。これは、演算子>が、これを数値の比較ではなく、文字列の比較とみなすためです。
整数値を確実に比較するには、intval(Q0.NAOK) > 50を使用します。Q0.NAOKが数値でない(空または文字列)場合は、intval(Q0.NAOK) === 0となります。文字列値を比較する("A" < "B")場合は、直接strcmpを使用します。strcmp(Q0.NAOK,"B")またはstrcmp(Q0.NAOK,"A5")
代入演算子(=)を使用する際の注意
代入演算子は、予期せぬ副作用を引き起こす可能性があるため、絶対に必要でない限り、使用しないでください。たとえば、先行する回答の値を変更した場合、その質問と現在の質問との間のカスケードされた出現条件と検証ロジックは再計算されないため、内部的に一貫性のないデータになりえます(たとえば、NULLであるべきものに回答が残る、回答すべきなのにスキップされる、など)。一般に、変数に値を割り当てる場合は、式の質問タイプを作成し、その値を設定するための式を使用する必要があります。しかし、本当に必要なことがまれにあるため、この演算子が用意されています。
この演算子について注意を促すため、構文式の中では赤いフォントで表示されています("=="と混同しないようにするため)。
代入演算子を使用する
代入演算子を使用する主な理由は次のとおりです。
- 既定値を設定できない質問の既定値を式を使って設定する必要がある(ユーザーインターフェイスでは回答オプションの1つを選択できるが、式を入力することができないリスト、ラジオなど)。ただし、LimeSurveyは式がその質問に対する許容可能な回答を生成できるかどうかを検証できないため、注意して使用してください。
- 後続の回答に基づいて先行する質問への回答を強制的に変更する必要がある
- など...
この目的のために、式マネージャーシステムを使用することができます。この目的のため、式を使用する方がよいでしょう。
例:
- 質問への回答を小文字にする:
{QCODE=strtolower(QCODE.NAOK)} - アンケートの開始時に配列質問タイプに既定の回答を設定する:
{Q1_SQ1=(is_empty(Q1_SQ1.NAOK),"A99",Q1_SQ1.NAOK)} - アンケート開始時に配列テキストの質問タイプに対する既定の回答を設定する:
{Q1_SQY1_SQX1 = (is_empty(Q1_SQY1_SQX1.NAOK),"Inserted answer", Q1_SQY1_SQX1.NAOK)} - 条件付きの回答を設定する:
{QCODE=if(YesNo="Y","A1","")}
XSS セキュリティ
XSSを有効にすると、式マネージャーシステムの一部がつかえなくなります。
- 式でHTMLタグを開き、別の式で閉じる
- URL内で複雑な式を使用する
例と解決策
{if( 1 ,"<strong>","")}information{if( 1 ,"</strong>","")}はXSSでは正常に動作しないため、次のようにします。{if(1,"<strong>information</strong>","information")}<a href="/script.php?value={if(QCODE == "Y","yes","no")}">next</a>は、ここでは式の質問を使います。なぜなら、完全な質問コードがOKだからです。<a href="/script.php?value={EQUATION.NAOK}">next</a>
変数へのアクセス
ExpressionScriptでは、必要な変数に読み取り専用でアクセスできます。下位互換性を保つため、次のものにアクセスすることができます。
- TOKEN:xxx - トークンの属性値(例: TOKEN:FIRSTNAME、TOKEN:ATTRIBUTE_5)(匿名でないアンケート向け)
- INSERTANS:SGQA - 回答として表示する値(例: "はい")。{QCODE.shown}と同じです。
- テンプレート内で使われるすべての{XXX}
- 質問テキストでは、{QID}を質問IDで置き換え、{SGQ}を質問のSGQAで置き換えることができます。
さらに、ExpressionScriptでは、質問コード(データベース内の質問テーブルの'タイトル'列)で変数を参照できます。これは、データをSPSS、R、またはSASにエクスポートするときに使用される変数ラベルでもあります。例えば、名前、年齢、性別について質問がある場合、12345X13X22、12345X13X23、12345X13X24といった形ではなく、name、age、genderといった形で変数を呼び出すことができます。これにより、式が読みやすく、ロジックが検証しやすくなり、また、グループや質問の番号を把握することなく質問をシャッフルすることが可能になります。
重要: 先行するページや質問で発生する変数を参照するのが安全です。
さらに、ExpressionScriptを使用すると、多くの質問プロパティにアクセスできます。
| Syntax | Meaning | Example | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qcode | an alias for Qcode.code | {implode(',',name,gender)} | 'Tom','M' |
| Qcode.code | the selected response code for the question if it is relevant (otherwise blank), or the text value if it is not a coded question | {implode(',',name.code,gender.code)} | 'Tom','M' |
| Qcode.NAOK | same as Qcode - see discussion of NAOK | {gender.NAOK} | 'M' |
| Qcode.value | the assessment value for the question if it is relevant (otherwise blank), or the text value if it is not a coded question | {gender.value} | '1' |
| Qcode.valueNAOK | same as Qcode.value - see discussion about NAOK | {gender.valueNAOK} | '1' |
| Qcode.shown | the display value for the question | {implode(',',name.shown,gender.shown)} | 'Tom','Male' |
| Qcode.question | the text of the question | {gender.question} | 'What is your gender?' |
| Qcode.mandatory | whether the question is mandatory (Y/N) | {gender.mandatory} | 'N' |
| Qcode.qid | the internal question number (not the sequential number) | {gender.qid} | 337 |
| Qcode.type | the question type | {gender.type} | 'G' |
| Qcode.jsName | the correct javascript name for the question, regardless whether declared on or off this page | {gender.jsName} | 'java1827X3X337' |
| Qcode.gid | the internal group number (not the sequential number) | {gender.gid} | 3 |
| Qcode.qseq | the sequential number of the question, starting from 0 | {gender.qseq} | 5 |
| Qcode.gseq | the sequential number of the group, starting from 0 | {gender.gseq} | 1 |
| Qcode.relevanceStatus | whether the question is currently relevant (0 or 1) | {gender.relevanceStatus} | 1 |
| Qcode.relevance | the question-level relevance equation | {gender.relevance} | '!is_empty(name)' |
| Qcode.grelevance | the group-level relevance equation | {gender.grelevance} | 'num_children >= 5' |
| Qcode.sgqa | the SGQA value for this question | {gender.sgqa} | '1827X3X337' |
HTMLエディターの問題
HTMLエディターを使用すると、一部の文字がHTML実体に置き換えられます。
- & → &
- < → <
- > → >
HTMLエディターを使用する場合は、次のものを使用する必要があります。
- & に対しては and
- < に対してはlt
- <= に対してはle
- > に対してはgt
- >= に対してはge
式の中のHTML表現を消去することをお勧めします。 LimeSurvey HTMLエディターを使用する場合は、エディターの左上にある"ソース"ボタンをクリックして、式に関連しないすべての文字を削除します(例:
、
など)。
Qcode変数の命名
Qcodeを構成する方法(およびいくつかのプロパティにアクセスする方法)の質問タイプ別の詳細は次のとおりです。一般に、Qcodeは次のように構成されます。
QuestionCode . '_' . SubQuestionID . '_' . ScaleId
commentとotherの場合、対応する質問コードはそれぞれQuestionCode_comment、QuestionCode_otherです。
| Type | Description | Code | SubQs | Answer Options | Scales | Answer Code | Answer Shown | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 Point Choice Radio-Buttons | Q1 | 1-5 | {Q1} | {Q1.shown} | {Q1==3} | ||
| B | Array (10 Point Choice) Radio-Buttons | Q2 | L1-L6 | 1-10 | {Q2_L2} | {Q2_L2.shown} | {Q2_L2==7} | |
| A | Array (5 Point Choice) Radio-Buttons | Q3 | 1-5 | 1-5 | {Q3_1} | {Q3_1.shown} | {Q3_1>=3} | |
| 1 | Array (Flexible Labels) Dual Scale | Q4 | sq1-sq5 | 0:a1-a3 | 1:b1-b3 | {Q4_sq1_0} | {Q4_sq1_1.shown} | {Q4_sq1_1=='b2'} |
| H | Array (Flexible) - Column Format | Q5 | 1-5 | s,m,t | {Q5_1} | {Q5_1.shown} | {Q5_1=='s'} | |
| F | Array (Flexible) - Row Format | Q6 | F1-F5 | 1-5 | {Q6_F3} | {Q6_F3.shown} | {Q6_F3==4} | |
| E | Array (Increase/Same/Decrease) Radio-Buttons | Q7 | 1-7 | I,S,D | {Q7_4} | {Q7_4.shown} | {Q7_4=='D'} | |
| : | Array (Multi Flexi) 1 To 10 | Q8 | ls1,todo,ls2 | min,max,avg | {Q8_ls1_max} | {Q8_ls2_avg.shown} | {Q8_ls2_min==7} | |
| ; | Array (Multi Flexi) Text | Q9 | hp,st,sw | 1st,2nd,3rd | {Q9_hp_3rd} | {Q9_hp_3rd.shown} | {Q9_hp_3rd=='Peter'} | |
| C | Array (Yes/Uncertain/No) Radio-Buttons | Q10 | 1-5 | Y,N,U | {Q10_1} | {Q10_1.shown} | {Q10_3=='Y'} | |
| X | Boilerplate Question | Q11 | {Q11.shown} | |||||
| D | Date | Q12 | {Q12} | {Q12.shown} | ||||
| * | Equation | Q13 | {Q13} | {Q13.shown} | {Q13>5} | |||
| ~124~ | File Upload (records number of files uploaded) | Q14 | {Q14} | {Q14>0} | ||||
| G | Gender Drop-Down List | Q15 | M,F | {Q15} | {Q15.shown} | {Q15=='M'} | ||
| U | Huge Free Text | Q16 | {Q16} | {Q16.shown} | {strlen(Q16)>100} | |||
| I | Language Question | Q17 | {Q17} | {Q17.shown} | {Q17=='en'} | |||
| ! | List - Dropdown | Q18 | 1-5 | {Q18} | {Q18.shown} | {Q18==3} | ||
| L | List Drop-Down/Radio-Button List | Q19 | A-Z | {Q19} | {Q19.shown} | {Q19=='X'} | ||
| O | List With Comment Drop-Down/Radio-Button List + Textarea | Q20 | A-F | {Q20},{Q20comment} | {Q20.shown} | {Q20=='B'} | ||
| T | Long Free Text | Q21 | {Q21} | {Q21.shown} | {strstr(Q21,'hello')>0} | |||
| M | Multiple Choice Checkbox | Q22 | A-F, other | {Q22_E}, {Q22_other} | {Q22_E.shown}, {Q22_other.shown} | {Q22_E=='Y'} | ||
| P | Multiple Choice With Comments Checkbox + Text | Q23 | A-F | {Q23_D}, {Q23_Dcomment} | {Q23_D.shown} | {!is_empty(Q23)} | ||
| K | Multiple Numerical Question | Q24 | self,mom,dad | {Q24_self} | {Q24_self.shown} | {Q24_self>30} | ||
| Q | Multiple Short Text | Q25 | A-F | {Q25_B} | {Q25_B.shown} | {substr(Q25_B,1,1)=='Q'} | ||
| N | Numerical Question Type | Q26 | {Q26} | {Q26.shown} | {Q26 > 30} | |||
| R | Ranking Style | Q27 | 1-4 | {Q27_1} | {Q27_1.shown} | {Q27_1==3} | ||
| S | Short Free Text | Q28 | {Q28} | {Q28.shown} | {Q28=='mine'} | |||
| Y | Yes/No Radio-Buttons | Q29 | {Q29} | {Q29.shown} | {Q29=='Y'} |
NAOKの利用
NAOK --> "Not Applicable"(該当なし、NA)は問題ない(OK)
NAOKは、すべてまたは一部の変数が出現条件を満たさないということです。"Not Applicable"(該当なし、NA)は問題ない(OK)。
例: count(Q1_SQ1,Q1_SQ2,Q1_SQ3,Q1_SQ4) は、Q1のサブ質問の一つがフィルターされている場合、常に空文字となります。このような質問で、チェックされたサブ質問の数をカウントするには、count(Q1_SQ1.NAOK,Q1_SQ2.NAOK,Q1_SQ3.NAOK,Q1_SQ4.NAOK)とします。サブ質問が隠されている場合、式マネージャーは空文字を返します。
NAOKがない場合、1つの質問または1つのサブ質問が非表示になっている場合、式マネージャーは常に空の文字列を返します(falseを返すのと同じです)。
.shownは常にNAOKの仕組み(非表示の時は空文字)を使っていますが、回答のコードが必要な場合は、質問コードの後に.NAOKを付加するとよいでしょう。それが必要で、内容を理解している場合は別です。
詳細は、入れ子条件の上書きの項にあります。
予約変数 "this"、"self"、"that"
回答されたサブ質問の数を数えたり、スコアを合計するなど、質問の全体を評価したい場合がよくあります。また、質問の特定の行や列(行や列の合計を取得してデータベースに格納するなど)を処理したい場合もあります。以下の予約変数により、そのプロセスを簡単に実現できます。
変数"This"
The "this" variable is used exclusively within the "Whole question validation equation" and "Subquestion validation equation" options (the later is not possible from GUI). It expands to the variable names of each of the cells within those questions. So, if you want to make sure that each entry is greater than three, you would set the "Subquestion validation equation" to (this > 3).
変数"Self"
"self"と"that"変数はより強力で、式を処理する前に展開されるマクロとして機能します。"self"変数の構文は次のとおりです。
- self
- self.suffix
- self.sub-selector
- self.sub-selector.suffix
- suffixは、通常のqcode接尾辞のいずれかです(例: NAOK、value、shown)。
- sub-selector can be one of the following:
- comments - only subquestions that are comments (e.g., multiple choice with comment and list with comment);
- nocomments - only subquestions that are not comments;
- sq_X - where X is a row or column identifier. Only subquestions matching pattern X are selected. Note that search is done on complete code identifier, then sq_X match and include subquestions nX, X, Xn (e.g. if you use sq_1, subquestions a1, 1a, 1, 11 or 001 was included). Put attention at dual scale question type where subquestions code are QCODE_SQCODE_1 and QCODE_SQCODE_1 and to ranking question type where subquestions code are QCODE_1,QCODE_2 ....
例:
- 質問に対して何らかの回答があったか? -> {count(self.NAOK)>0}
- この質問の評価点数は? -> {sum(self.value)}
行と列の合計を取得することもできます。列A-Eと行1-5の数字の配列があるとします。
- 総合計は? -> {sum(self.NAOK)}
- 列Bの合計は? -> {sum(self.sq_B.NAOK)}
- 行3の合計は? -> {sum(self.sq_3.NAOK)}
変数"That"
"that"は"self"に似ていますが、他の質問を参照することができます。構文は次のとおりです。
- that.qname
- that.qname.suffix
- that.qname.sub-selector
- that.qname.sub-selector.suffix
qnameは、サブ質問拡張がない質問の名前です。質問 'q1'を作成したら、それがqnameとなります。
例:
- 質問q1に対して何らかの回答があったか? -> {count(that.q1.NAOK)>0}
- q2の評価点数は? -> {sum(that.q2.NAOK)}
- q3の総合計は? -> {sum(that.q3.NAOK)}
- q4の列Cの合計は? -> {sum(that.q4.sq_C.NAOK)}
- q4の行2の合計は? -> {sum(that.q4.sq_2.NAOK)}
"self"と"that"変数は、出現条件、検証、文言調整の式で使用できます。
The one caveat is that when you use the Show logic file feature, it will show you the expanded value of "self" and "that". This lets you see the actual equation that will be generated so that you (and the EM) can validate whether the variables exist or not. This may seem confusing since you may see quite lengthy equations. However, if you edit the question, you will see the original equation using "self" and/or "that".
- you want to explicitly name each variable used in an equation, or
- use variables that do not have subquestions (e.g., single response questions). In those cases, prefixing a variable with "that" is overkill, and you run the risk of getting unexpected results.
関数へのアクセス
The ExpressionScript provides access to mathematical, string, and user-defined functions, as shown below. It has PHP and JavaScript equivalents for these functions so that they work identically on server-side (PHP) and client-side (JavaScript). It is easy to add new functions.
Implemented functions
The following functions are currently available:
| Function | Meaning | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| abs | Absolute value | number abs(number) |
| acos | Arc cosine | number acos(number) |
| addslashes | Quote string with slashes | string addslashes(string) |
| asin | Arc sine | number asin(number) |
| atan | Arc tangent | number atan(number) |
| atan2 | Arc tangent of two variables | number atan2(number, number) |
| ceil | Round fractions up | number ceil(number) |
| checkdate | Returns true(1) if it is a valid date in gregorian calendar | bool checkdate(month,day,year) |
| convert_value | Convert a numerical value using a inputTable and outputTable of numerical values | number convert_value(fValue, iStrict, sTranslateFromList, sTranslateToList) |
| cos | Cosine | number cos(number) |
| count | count the number of answered (non-blank) questions in the list | number count(arg1, arg12, ..., argN) |
| countif | Count the number of answered questions in the list equal to the first argument | number countif(matches, arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| countifop | Count the number of answered questions in the list which pass the criteria (arg op value) | number countifop(op, value, arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| date | Format a local date/time | string date(format [, timestamp=time()]) |
| exp | Calculates the exponent of e | number exp(number) |
| fixnum | Display numbers with comma as radix separator, if needed | string fixnum(number) |
| floor | Round fractions down | number floor(number) |
| gmdate | Format a GMT date/time | string gmdate(format [, timestamp=time()]) |
| html_entity_decode | Convert all HTML entities to their applicable characters (always uses ENT_QUOTES and UTF-8) | string html_entity_decode(string) |
| htmlentities | Convert all applicable characters to HTML entities (always uses ENT_QUOTES and UTF-8) | string htmlentities(string) |
| expr_mgr_htmlspecialchars | Convert special characters to HTML entities (always uses ENT_QUOTES and UTF-8) | string htmlspecialchars(string) |
| expr_mgr_htmlspecialchars_decode | Convert special HTML entities back to characters (always uses ENT_QUOTES and UTF-8) | string htmlspecialchars_decode(string) |
| idate | Format a local time/date as integer | string idate(string [, timestamp=time()]) |
| if | Excel-style if(test,result_if_true,result_if_false) | if(test,result_if_true,result_if_false) |
| implode | Join array elements with a string | string implode(glue,arg1,arg2,...,argN) |
| intval | Get the integer value of a variable | int intval(number [, base=10]) |
| is_empty | Determine whether a variable is considered to be empty | bool is_empty(var) |
| is_float | Finds whether the type of a variable is float | bool is_float(var) |
| is_int | Find whether the type of a variable is integer | bool is_int(var) |
| is_nan | Finds whether a value is not a number | bool is_nan(var) |
| is_null | Finds whether a variable is NULL | bool is_null(var) |
| is_numeric | Finds whether a variable is a number or a numeric string | bool is_numeric(var) |
| is_string | Find whether the type of a variable is string | bool is_string(var) |
| join (New in 2.0 build 130129) | Join elements as a new string | join(arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| list | Return comma-separated list of non-blank values | string list(arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| listifop (New in 3.16.1 ) | Return a 'glue'-separated list of the specified question property (retProp) from questions in the list which pass the criteria (cmpProp op value) | string listifop(cmpProp, op, value, retProp, glue, sgqa1, sgqa2, ... sgqaN) |
| ltrim | Strip whitespace (or other characters) from the beginning of a string | string ltrim(string [, charlist]) |
| max | Find highest value | number max(arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| min | Find lowest value | number min(arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| mktime | Get UNIX timestamp for a date (each of the 6 arguments are optional) | number mktime([hour [, minute [, second [, month [, day [, year ]]]]]]) |
| modulo-function | The modulo function is not supported yet. You can use the floor() function instead | floor(x/y)==(x/y) |
| nl2br | Inserts HTML line breaks before all newlines in a string | string nl2br(string) |
| number_format | Format a number with grouped thousands | string number_format(number) |
| pi | Get value of pi | number pi() |
| pow | Exponential expression | number pow(base, exp) |
| quoted_printable_decode | Convert a quoted-printable string to an 8 bit string | string quoted_printable_decode(string) |
| quoted_printable_encode | Convert a 8 bit string to a quoted-printable string | string quoted_printable_encode(string) |
| quotemeta | Quote meta characters | string quotemeta(string) |
| rand | Generate a random integer, see this example | int rand() OR int rand(min, max) |
| regexMatch | compare a string to a regular expression | bool regexMatch(pattern,input) |
| round | Rounds a number to an optional precision | number round(val [, precision]) |
| rtrim | Strip whitespace (or other characters) from the end of a string | string rtrim(string [, charlist]) |
| sin | Sine | number sin(arg) |
| sprintf | Return a formatted string | string sprintf(format, arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| sqrt | Square root | number sqrt(arg) |
| stddev | Calculate the Sample Standard Deviation for the list of numbers | number stddev(arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| str_pad | Pad a string to a certain length with another string | string str_pad(input, pad_length [, pad_string]) |
| str_repeat | Repeat a string | string str_repeat(input, multiplier) |
| str_replace | Replace all occurrences of the search string with the replacement string | string str_replace(search, replace, subject) |
| strcasecmp | Binary safe case-insensitive string comparison | int strcasecmp(str1, str2) |
| strcmp | Binary safe string comparison | int strcmp(str1, str2) |
| strip_tags | Strip HTML and PHP tags from a string | string strip_tags(str, allowable_tags) |
| stripos | Find position of first occurrence of a case-insensitive unicode string (starting by 0, return false if not found) | int stripos(haystack, needle [, offset=0]) |
| stripslashes | Un-quotes a quoted string | string stripslashes(string) |
| stristr | Case-insensitive strstr | string stristr(haystack, needle [, before_needle=false]) |
| strlen | Get string length | int strlen(string) |
| strpos | Find position of first occurrence of an unicode string (starting by 0, return false if not found) | int strpos(haystack, needle [ offset=0]) |
| strrev | Reverse a string | string strrev(string) |
| strstr | Find first occurrence of a string | string strstr(haystack, needle[, before_needle=false]) |
| strtolower | Make a string lowercase | string strtolower(string) |
| strtotime | Parse about any English textual datetime description into a Unix timestamp | int strtotime(string) |
| strtoupper | Make a string uppercase | string strtoupper(string) |
| substr | Return part of an unicode string | string substr(string, start [, length]) |
| sum | Calculate the sum of values in an array | number sum(arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| sumifop | Sum the values of answered questions in the list which pass the criteria (arg op value) | number sumifop(op, value, arg1, arg2, ... argN) |
| tan | Tangent | number tan(arg) |
| time | Return current UNIX timestamp | number time() |
| trim | Strip whitespace (or other characters) from the beginning and end of a string | string trim(string [, charlist]) |
| ucwords | Uppercase the first character of each word in a string | string ucwords(string) |
| unique | Returns true if all non-empty responses are unique | boolean unique(arg1, ..., argN) |
ExpressionScript knows which variables are local
In order to properly build the JavaScript for a page, EM needs to know which variables are set on the page, and what their JavaScript ID is (e.g., for document.getElementById(x)). It must also know which variables are set on other pages (so that it can ensure that the needed <input type='hidden' value='x'> fields are present and populated).
Cascading Conditions
If any of the variables are irrelevant, the whole equation will be irrelevant (false). For example, in the following table, N/A means that one of the variables was not relevant:
| Operator | Example | a | b | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + (unary) | +a | N/A | false | |
| ! | !a | N/A | false | |
| == (or eq) | a == b | N/A | 5 | false |
| == (or eq) | a == b | N/A | 0 | false |
| == (or eq) | a == b | N/A | N/A | false |
| != (or ne) | a != b | N/A | 5 | false |
| != (or ne) | a != b | N/A | N/A | false |
| != (or ne) | a != b | N/A | 0 | false |
| > (or gt) | a > b | N/A | 5 | false |
| >= (or ge) | a >= b | N/A | 5 | false |
| < (or lt) | a < b | N/A | 5 | false |
| <= (or le) | a <= b | N/A | 5 | false |
| and | a and b | N/A | 5 | false |
| and | a and b | N/A | N/A | false |
| or | a or b | N/A | N/A | false |
| or | a or b | N/A | 5 | false |
| + | a + b | N/A | 5 | false |
| * | a * b | N/A | 5 | false |
| / | a / b | 5 | N/A | false |
| () | (a) | N/A | false | |
| (exp) | (a && b) | N/A | 5 | false |
| (exp) op (exp) | (b + b) > (a && b) | N/A | 5 | false |
| function | sum(a,b,b) | N/A | 5 | false |
| function | max(a,b) | N/A | 5 | false |
| function | min(a,b) | N/A | 5 | false |
| function | implode(', ',a,b,a,b) | N/A | 5 | false |
| function | if(a,a,b) | N/A | 5 | false |
| function | is_empty(a) | N/A | false | |
| function | is_empty(a) | 0 (or blank) | true | |
| function | !is_empty(a) | N/A | false |
入れ子条件の上書き
出現条件を満たした回答の合計を表示したいとします。式 {sum(q1,q2,q3,...,qN)}を使おうとするでしょう。しかし、これは内部的にLEMif(LEManyNA("q1","q2","q3",...,"qN"),"",sum(LEMval("q1"),LEMval("q2"),LEMval("q3"),...,LEMval("qN")))に変換されます。これにより、値q1〜qNのいずれかが出現条件を満たさない場合、式は常にfalseを返します。この場合、sum()はすべての質問が出現して回答されない限り"0"となります。
この問題を回避するために、各変数には".NAOK"という接尾辞(「Not Applicable」はOK)を追加することができます。このような場合、次のような現象が発生します。変数q1.NAOKがあるとします。
- q1はLEManyNA()節には追加されません
- LEMval('q1')は回答が出現条件を満たしているかを確認し、そうでない場合は""を返します(出現条件を満たさない回答は無視されますが、式全体を無効にしません)。
したがって、合計を求める方法は、次の式となります。sum(q1.NAOK,q2.NAOK,q3.NAOK,...,qN.NAOK)
The use of the .NAOK suffix also lets authors design surveys that have several possible paths but then converge on common paths later. For example, say subjects answer a survey in a way that is outside the normal range of responses. The author could alert the subjects that they may not get valid results, and ask them whether they really want to continue with the survey. If they say "Yes", then the rest of the questions will be shown. The condition for the "rest of the questions" would check whether the initial responses were answered within the normal range OR whether the subject said "Yes" to the question that is only relevant if they answered outside the normal range.
How does ExpressionScript support conditional micro-tailoring?
ここでは、カスタマイズ(質問タイプ'expr'は式を意味します)の例を示します。
| Question Code | Relevance | Question Type | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | 1 | text | What is your name? |
| age | 1 | text | How old are you? |
| badage | !is_empty(age) | expr | {(age<16) or (age>80)} |
| agestop | badage | message | Sorry, {name}, you are too {if( (age<16),'young',if( (age>80),'old','middle-aged') ) } for this test. |
| kids | !badage | yesno | Do you have children? |
| parents | 1 | expr | {!badage && kids=='Y'} |
| numKids | parents | text | How many children do you have? |
| kid1 | parents && numKids >= 1 | text | How old is your first child? |
| kid2 | parents && numKids >= 2 | text | How old is your second child? |
| kid3 | parents && numKids >= 3 | text | How old is your third child? |
| kid4 | parents && numKids >= 4 | text | How old is your fourth child? |
| kid5 | parents && numKids >= 5 | text | How old is your fifth child? |
| sumage | 1 | expr | {sum(kid1.NAOK,kid2.NAOK,kid3.NAOK,kid4.NAOK,kid5.NAOK)} |
| report | parents | text | {name}, you said you are {age} and that you have {numKids}. The sum of ages of your first {min(numKids,5)} kids is {sumage} |
このアンケート例をダウンロードするには、次のリンクをクリックしてください。子供の数のアンケート例
All of these questions can be on a single page (e.g., in the same group), and only the relevant questions will be displayed. Moreover, as you enter the ages of children, the sum() expression in the last question will dynamically get updated.
ExpressionScript provides this functionality by surrounding each expression with a named <span> element. Every time a value changes, it recomputes the expression that should appear in that <span> element and regenerates the display. You can have dozens or even hundreds of such tailored expressions on the same page.
構文ハイライト
To help with entering and validating expressions, the EM provides syntax highlighting with the following features:
Types and Meanings of Syntax Highlighting
| Color | Sample | Meaning | Tooltip | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tan background | Sample | the whole equation | none | Anything within curly braces that is recognized as an equation (e.g., there is no leading or trailing whitepace) will be color-coded with a tan background to help distinguish it from surrounding text |
| bold red text | Sample | An error | Some explanation on error | Can be an unknow variable or an error in function. Survey is broken and the questions that rely on the respective expression will not be shown to the respondents. |
| blue text | Sample | function name | meaning and allowable syntax | It refers to function names or things that should be functions since they are followed by an open parenthesis. They are displayed in bold blue text. Tooltips show the meaning and allowable syntax for the function. |
| grey text | Sample | string | none | Single and double-quoted strings are shown in grey text. |
| cyan text | Sample | variable set on the same page, | [name or SGQA code]: question; value; answerList showing codes for each value | Any variable that is set on the same page as the question you are currently editing is shown in cyan text (it can be updated in javascript). The tooltip shows its name (if you used INSERTANS:xxx) or its SGQA code (if you used the new naming system), the actual question, and its current value (or blank if not set). If the question type expects responses from an enumerated value set, the mapping of the codes to display values is shown. |
| green text | Sample | variable set on a prior page | [name or SGQA code]: question; value; answerList showing codes for each value | Any variable that is set on a prior page is shown in bold green text. The tooltip shows its name (if you used INSERTANS:xxx) or SGQA code (if you used the new naming system), the actual question, and its current value (or blank if not set). If the question type expects responses from an enumerated value set, the mapping of the codes to display values is shown. |
| bold pink text | Sample | variable set on a later page in general : empty at survey start, but can be filled with index or move previous | [name or SGQA code]: question; value; answerList showing codes for each value | Any variable that is set on a prior page is shown in bold pink text. The tooltip shows its name (if you used INSERTANS:xxx) or SGQA code (if you used the new naming system), the actual question, and its current value (or blank if not set). If the question type expects responses from an enumerated value set, the mapping of the codes to display values is show. |
| bold tan text | Sample | a lime replacement value | the value | Lime Replacement Strings (like {TOKEN:xxx}, {PRIVACY_MESSAGE}) are shown in bold tan text. |
| red text | Sample | assignment operator (=) | warning message | If you use one of the assignment operator (=), that operator will be displayed in red text. This is meant to help prevent accidental re-assignment of values when you really meant to check whether a == b instead of setting the value of a = b. |
| normal black text | Sample | punctuation | none | All other punctuation signs within the expression are shown as normal black text. |
| red-boxed text | a bold red line surrounds the error | syntax error | description of the error | Any detected syntax errors are shown within red boxes. The tooltip shows the error. Examples include unmatched parentheses, use of undefined functions, passing the wrong number of arguments to functions, poorly structured expressions (e.g., missing operators between variables), trying to assign a new value to a read-only variable, trying to assign values to non-variables, or using unsupported syntax. Note that the syntax error dectection system may only report one error in an expression even if there are multiple errors; however, if any errors are detected, at least one error will be shown. |